- Home
- Knee Pain Diagnosis
- Stiff Knee
Stiff Knee
Written By: Chloe Wilson, BSc(Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed by: KPE Medical Review Board
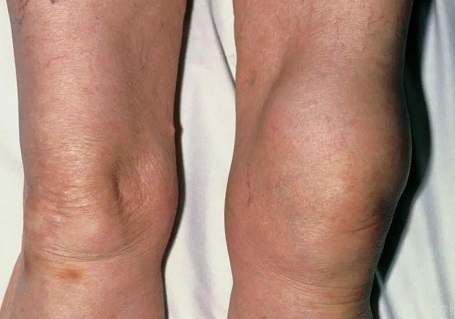
Having a stiff knee can have a big impact on your life. Not only does it limit knee movement, it is often painful and affects your day to day activities.
Knee stiffness can develop for a number of reasons. There may be a problem in the joint restricting movement, weakness or tightness in the surrounding muscles, or swelling.
A stiff knee may be caused by a knee injury, medical condition, muscle imbalance or altered knee biomechanics.
Here we will look at the most common causes of knee stiffness and how to treat them and improve knee flexibility.
Common Causes of A Stiff Knee
The most common causes of a stiff knee are:
- Meniscus Injuries: damage to the knee cartilage
- Ligament Injuries: damage to the ACL, PCL, MCL or LCL
- Fractures: damage to one of the knee bones
- Tendonitis: inflammation or degeneration of one of the knee tendons
- Knee Arthritis: wear and tear in the knee joint
- Knee Bursitis: inflammation of one of the knee bursa
- Gout Knee: an inflammatory arthritis causing joint crystal formation
There are also some other causes of stiff knee pain that are fairly rare including arthrofibrosis, post exercise stiffness, tumors and infections.
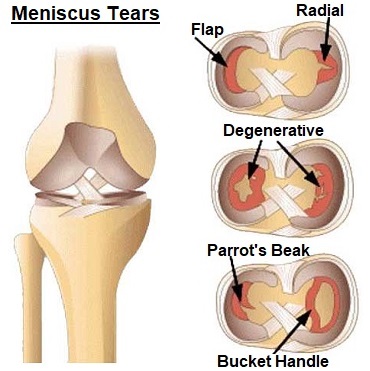
1. Meniscus Injuries
A meniscus tear is one of the most common causes of a stiff knee.
A meniscus injury is where there is damage to the special cartilage that lines the knee joint. This can cause knee stiffness by preventing the smooth motion of the joint.
Sometimes a fragment of damaged cartilage can even get stuck in the joint, restricting movement, known as knee locking.
Knee stiffness from a meniscus tear is usually treated with a combination of PRICE, strengthening and stretching exercises, knee injections and in some cases surgery.
Find out more about the common causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options to reduce stiff knee pain in the Meniscus Tears section.
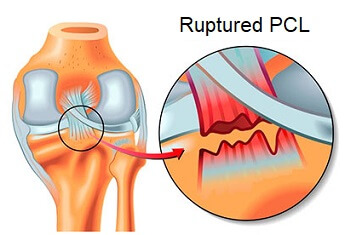
2. Knee Ligament Injuries
Another common cause of stiff knee pain is a ligament injury, aka knee sprain.
Ligaments are tough, fibrous bands that provide stability to the knee. If one or more of the knee ligaments are overstretched, then some or all of the fibers may tear.
This leads to bleeding and swelling in the knee joint which inhibits movement resulting in stiff knee pain. Knee stiffness may persist, even once the swelling settles down if the ligament doesn't get the right treatment as it may not heal properly.
If the ligament ruptures completely, then knee swelling usually comes on immediately and is profuse which can really restrict knee movement.
Find out more about the causes, symptoms and stiff knee treatment options in the knee sprain section.
3. Bone Fractures
A break or fracture in any of the knee bones can also cause knee stiffness due to pain, instability and misalignment. Not only will knee movement be limited immediately after knee or patella fractures, but even once it has healed or been surgically fixed, knee stiffness often persists.
It is therefore really important to work hard at your rehab program if you have broken your knee to help reduce the swelling and prevent muscle tightening to reduce the risk of having to live with a long-term stiffness in the knee.
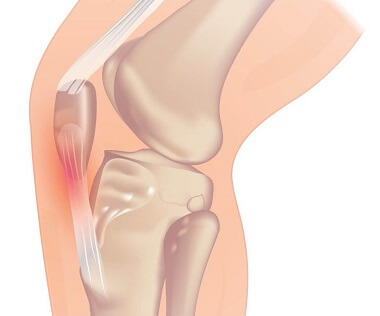
4. Knee Tendonitis
Knee tendonitis, where there is inflammation or degeneration of the knee tendons, is another common cause of knee stiffness, usually from overuse
Tendon damage can affect the pull on the knee joint, due to weakness and ineffectiveness, limiting its normal motion. The tendon may become inflamed or tight thus restricting knee motion range and resulting in a stiff knee.
Knee tendonitis most commonly occurs at the front of the knee, either above or below the knee cap:
- Patellar Tendonitis: aka Jumpers Knee affects the tendon which joins the kneecap to the shin bone
- Quads Tendonitis: affects the tendon that links the quadriceps to the kneecap
- Hamstring Tendonitis: affects the tendons at the back of the knee
You can find out all about the common causes, symptoms and treatment options for a stiff knee from tendonitis using the links above.
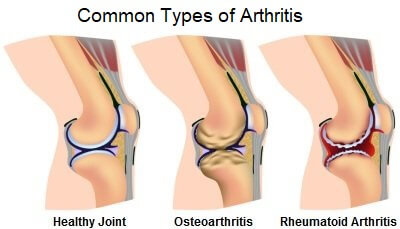
5. Knee Arthritis
Knee arthritis is the most common cause of knee stiffness in people over the age of 60. There are two main types of arthritis that can lead to a stiff knee.
Osteoarthritis, more commonly known as wear-and-tear arthritis, causes the breakdown of knee cartilage and bone. The joint loses its smooth surfaces and the space between the bones decreases. This reduces the amount the joint is able to move, leading to a stiff knee.
Knee stiffness from osteoarthritis tends to be worse first thing in the morning or after prolonged rest, easing fairly quickly with movement. It typically only affects one or two joints.
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic, systemic disorder that causes inflammation and fibrosis of multiple joints. It can result in damage to the cartilage and bones causing knee stiffness, usually in both legs, and is often accompanied by redness, warmth and swelling.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis fluctuate, with good spells and bad spells. It tends to affect
multiple joints, such as the hands and feet as well as the knees.
Having arthritis doesn't mean you are destined to have stiff knee pain - there is lots that you can do to reduce knee stiffness such as exercises, using heat and changing your diet.
Find out more about the causes, symptoms, progression and treatment options for stiffness in the knee in the knee arthritis section.
6. Knee Bursitis
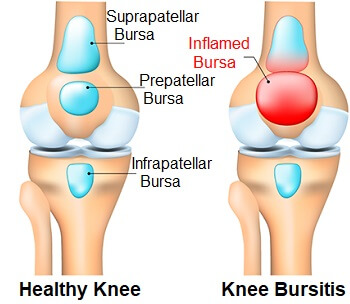
Bursitis is another common cause of knee stiffness and develops when there is swelling in one of the bursa, small fluid filled sacs that provide cushioning between bones and tendons around the knee.
Knee bursa can get inflamed either from excessive friction or a sudden blow that squashes them. Knee bursitis usually presents as a squashy lump, a bit like a small orange, and can occur at different point around the knee:
- Prepatellar Bursitis: at the front of the knee
- Pes Anserine Bursitis: on the inner knee
- Iliotibial Bursitis: on the outer knee
- Semimembranosus Bursitis: at the back of the knee
- Infrapatellar Bursitis: below the kneecap
- Suprapatellar Bursitis: above the knee
The influx of fluid prevents the knee from moving through its full range of movement which can result in stiff knee pain.
Find out more about the causes, symptoms and treatment options for bursitis knee stiffness in the knee bursitis section.
7. Gout Knee
Stiff knee pain may also be due to gout. Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis caused by a build-up of uric acid which deposits crystals, most commonly in the knees or feet.
Symptoms of gout knee come on rapidly over a few hours and as well as knee stiffness, the joint tends to also feel hot, very painful and looks red. It can be extremely uncomfortable to move the knee or bear any weight through it when gout flares up.
Gout knee is usually treated with medications, rest and ice. Episodes of gout usually settle down within a couple of weeks, but that is long enough for the knee to tighten up. Exercises are therefore really important after an episode of gout to avoid a stiff knee.
Find out more about the common causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention in the gout knee section.
Other Causes of Knee Stiffness
There are a few other possible causes of knee stiffness:
1. Arthrofibrosis
Arthofibrosis is a rare condition that can develop following a knee injury or surgery resulting in a stiff knee. Arthrofibrosis is a condition where the body develops excessive scar tissue adhesions which cause painful restriction to knee movement.
Carefully following your rehab program after a knee injury is the best way to reduce the risk of developing arthrofibrosis. In chronic cases, knee surgery may be required to remove the adhesions.
2. Post Exercise Stiffness
Some people find that they have a stiff knee after exercising. This doesn't necessarily mean they have an injury, they may have just overloaded their muscles.
Overworked muscles quickly become tight and weak making the leg feel
stiff. This is a common cause of knee stiffness in runners. The best way to avoid this is to warm up and cool down effectively when exercising, particularly focusing on knee stretches.
3. Rare Causes Of Knee Stiffness
There are a couple of rare causes of a stiff knee that are potentially very serious, and require immediate medical attention.
- Tumor: An abnormal growth in the bone
- Infection: Such as osteomyelitis (infection in the bone) or septic arthritis (infectious arthritis)
Why Do I Get Knee Stiffness?
Knee stiffness often develops after an injury or due to an underlying knee condition. A stiff knee is usually linked with:
1. Excess Fluid
When the knee is damaged, there is often a build-up of excess fluid inside the joint which can result in stiffness in the knee. The amount of knee swelling will depend on the severity of the injury.
With a minor knee injury, irritation inside the joint leads to increased production of synovial fluid.
Any excess fluid in the joint can result in a stiff knee as the fluid limits movement by taking up space in the joint and blocking the movement.
But knee swelling isn’t always visible, you can't always see it - there can be a considerable amount of excess fluid in the joint before there are any outward signs. So it is possible to have a stiff knee without any other symptoms.
With a more serious knee injury, such as an ACL rupture, there may be bleeding directly into the joint, known as a haemarthrosis which can result in considerable knee swelling and stiffness.
Reducing swelling is one of the best ways to treat a stiff knee and there are a number of different ways to treat a swollen knee.
2. Altered Knee Biomechanics
If one of the structures of the knee is damaged, it can change how the knee moves. There is a sophisticated system of gliding, rolling and spinning movements in the joint to achieve full range of movement.
Knee injuries and swelling often affect these movements, limiting the mobility at the joint, leading to a stiff knee. If you have ongoing knee stiffness, then a physical therapist can perform joint mobilization techniques to restore the normal motion at the knee.
3. Knee Pain Inhibition
Knee pain itself often leads to knee stiffness. It’s a normal reaction – when we move, it hurts, so we stop the movement. In the early stages following a knee injury, this response is helpful in preventing further damage. But if allowed to continue, the muscles and joint can become tight which can result in a chronic stiff knee.
In more severe injuries, knee pain may be so bad that it actually restricts knee movement altogether. In this case, the first thing to do is to get the pain and any swelling under control so it is worth talking to your doctor about medication that may help.
Stiff Knee Pain Treatment
Stiff knee treatment focuses on reducing pain and inflammation and regaining knee flexibility and mobility. In the early stages of knee stiffness, particularly after a knee injury, following PRICE principles can really help:
- Protect: the joint from further damage, e.g. with a brace.
- Rest: from aggravating activities, but keep the leg gently moving so it doesn’t seize up.
- Ice: regular ice treatment can help reduce swelling and therefore knee stiffness.
- Compression: specially designed bandages such as tubigrip help to support the knee and reduce swelling.
- Elevation: keeping the leg elevated helps excess fluid in the joint to drain away.
You can find out more about each of these in the PRICE treatment section.
Further stiff knee treatment will usually involve a combination of:
- Exercises: Stretching and strengthening exercises
- Heat: increases blood flow and can help loosen the knee
- Keeping Active: movement helps to reduce swelling and improve joint lubrication
- Medication: to get any pain and inflammation under control
- Dietary Changes: some foods increase inflammation, others help to decrease it
- Physical Therapy: e.g. joint mobilisation, rehab and acupuncture and
Find out loads more about how stiff knee treatment helps to improve knee flexibility, reduce knee stiffness and regain knee motion range.
Supplements For Knee Stiffness

There are various supplements that claim to reduce the symptoms of a stiff knee pain, particularly with arthritis.
The most popular ones include omega-3, glucosamine and chondroitin which can help to improve knee joint lubrication.
You can find out more about how taking supplements can help to reduce knee stiffness and how they work in the supplements section.
How Much Should The Knee Move?
The knee is designed to not only bend and straighten, but also to twist. A complex combination of gliding, spinning and rolling movements at the joint allows full, smooth, pain-free movement to occur without any knee stiffness.
Normal knee range of motion is the ability to move the joint through its full range without any pain or knee stiffness. Ideally, the knee should be able to bend and straighten from 0-145o and there should be around 40-50o of rotation.
Functionally, most activities don't require full range of flexion at the knee. For example, walking only needs around 65 degrees of flexion and going up and down stairs needs approximately 90 degrees flexion. But they do require full knee extension, so any knee stiffness into extension is going to start causing problems.
You can find out lots more about normal knee movement, how to measure it and what restricts it in the knee range of motion section.
Stiff Knee Summary
Knee stiffness is a common issue that can be caused by a variety of factors, such as injury, arthritis, overuse and muscle tightness. Treatment for stiff knee pain usually involves rest, physical therapy and medications such as anti-inflammatory and pain relievers. Recovery time will depend on the severity of the condition, but in general, it may take several weeks to months for the symptoms to fully subside.
Any new cases of a stiff knee, especially if the cause is unknown, should always be checked out by your doctor for an accurate diagnosis. The same is true if the knee swelling doesn't start to reduce after a couple of days. If you are not sure what is causing your knee stiffness, check out our knee pain diagnosis tools.
In most cases, the earlier stiff knee treatment begins, the quicker recovery tends to be, so early intervention is key for reducing knee swelling and to stop you getting a stiff knee.
You might also be interested in the following articles:
- Front Knee Pain
- Inner Knee Pain
- Outer Knee Pain
- Pain Behind The Knee
- Knee Pain & Popping
- Burning Knee Pain
- Knee Pain On Stairs
Page Last Updated: 05/10/23
Next Review Due: 05/10/25